Artificial Intelligence (AI) enables machines to learn from experiences, adapt to new inputs, and perform tasks resembling human activities. Most examples we hear about today, from computers playing chess to self-driving cars, rely heavily on deep learning and natural language processing.
Experts can train computers to accomplish specific tasks by processing vast amounts of data and recognizing patterns
using these technologies.
Artificial intelligence refers to computer systems capable of performing complex tasks that previously required human intellect, such as thinking, decision-making, and problem-solving. In our current era, “artificial intelligence” encompasses numerous technologies powering many services and products we use daily, from applications that recommend TV shows to chatbots providing real-time customer support.
But do all these examples represent AI as we envision it? If not, why do we frequently use the term?
In this article, you will learn about artificial intelligence, its evolution and history, what it does, and its various types.
History and Evolution of Artificial Intelligence
The roots of artificial intelligence date back to 1956, when the term was first coined. However, its popularity has significantly increased in the current era, thanks to the massive growth in data volumes, advancements in sophisticated algorithms, and improvements in computing and storage capabilities.
Early research in artificial intelligence during the 1950s explored problem-solving and symbolic methods. In the 1960s, the U.S. Department of Defense expressed interest in this type of research and began training computers to simulate basic human thinking.
For instance, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) completed street mapping projects in the 1970s and successfully developed intelligent personal assistants in 2003, before Siri, Alexa, and Cortana emerged.
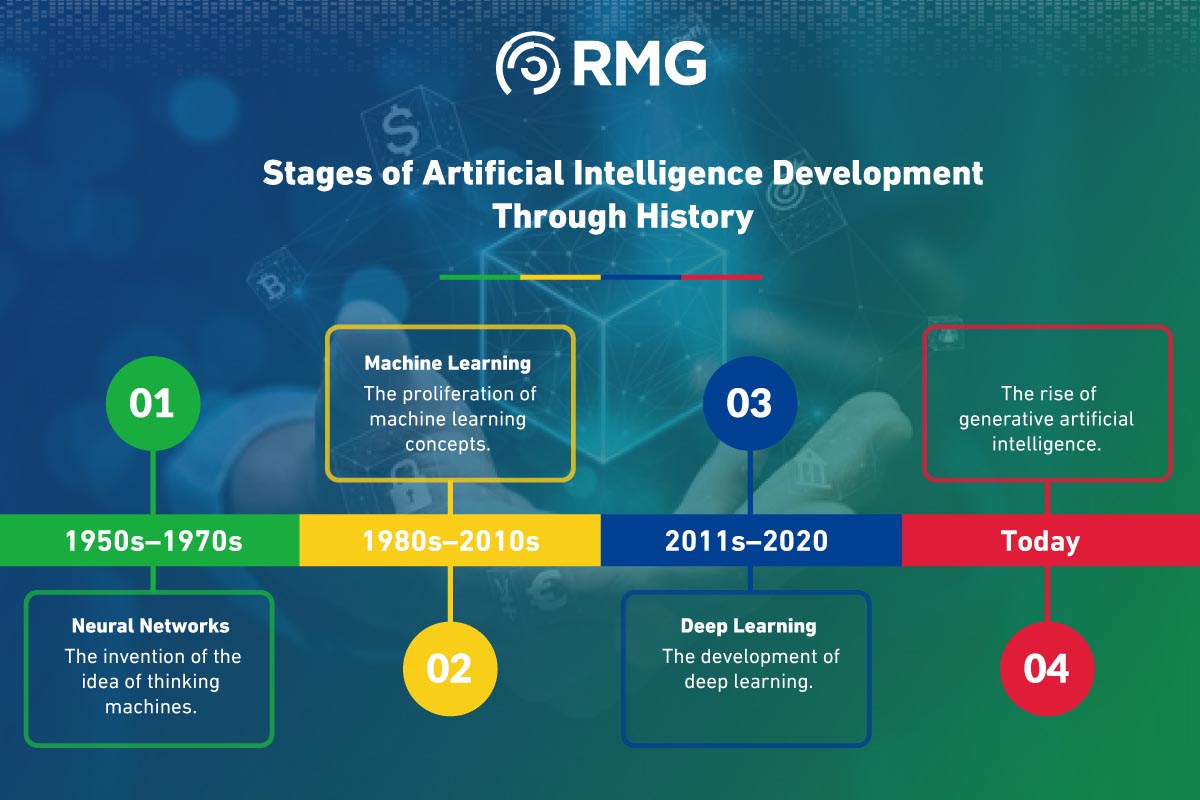
Key Stages in the Development of Artificial Intelligence
1950s–1970s: Neural Networks
Early work in neural networks sparked excitement for “thinking machines.”
1980s–2010s: Machine Learning
Machine learning became dominant, with the development of practical applications.
2011–2020s: Deep Learning
Breakthroughs in deep learning led to significant advances in artificial intelligence.
Today: Generative Artificial Intelligence
Generative AI is experiencing widespread adoption as an innovative technology reshaping the future.

What Are the Top 3 Digital Technologies That AI Relies On?
- Machine Learning
- Deep Learning
- Natural Language Processing

Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the theory and development of computer systems capable of performing tasks that previously required human intelligence, such as speech recognition, decision-making, and pattern detection.
AI is a broad term encompassing a variety of technologies, including machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing. While this term can describe many technologies in use today, there are differing opinions on whether these technologies truly represent artificial intelligence.
Some believe that most current applications represent advanced forms of machine learning, which are merely preliminary steps toward General Artificial Intelligence (GAI).
However, despite the philosophical debate over the existence of “intelligent machines,” most people using the term AI today refer to a range of technologies powered by machine learning, such as ChatGPT or computer vision, enabling machines to perform tasks that previously required human capabilities, like translation, content writing, idea generation, driving cars, and data analysis.
Artificial General Intelligence
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is a theoretical state where computer systems can achieve or surpass human intelligence levels. In other words, AGI is “real intelligence.” as portrayed in various articles, science fiction novels, television shows, movies, and comics.
However, there is no complete consensus among researchers on recognizing AGI when it appears. One of the most famous methods for testing machine intelligence is the “Turing Test,” or what is known as the imitation game, proposed by the renowned mathematician and computer scientist Alan Turing in a 1950 paper.
Turing described an experiment based on textual communication between a human “interrogator,” a machine, and another human, aiming to determine who wrote the responses.
If the interrogator cannot reliably distinguish between the human and the machine, the machine is considered intelligent according to Turing.
Overall, there is still disagreement among researchers and philosophers about whether we are actually getting closer to achieving AGI, or if it remains out of reach, or even entirely impossible.
For instance, while some recent studies from Microsoft Research and OpenAI suggest that ChatGPT-4 may be an early form of AGI, many researchers remain skeptical of these claims, viewing them as marketing-driven.
Regardless of how far we progress toward achieving AGI, it can be assumed that when using the term “Artificial General Intelligence,” it refers to programs and machines with cognitive abilities that we often encounter in popular science fiction works.

Types of Artificial Intelligence
As researchers strive to develop advanced forms of artificial intelligence, it becomes essential to gain a more precise understanding of what intelligence or even awareness truly means. In this context, we can categorize artificial intelligence into four main types, which we briefly outline as follows:
- Reactive Machines
Reactive machines are the simplest types of AI. They do not possess knowledge of past events and are limited to “reacting” to what is happening in front of them at the present moment.
For this reason, these machines can perform specific and advanced tasks within a very narrow scope but can’t execute any tasks outside this limited context.
- Limited Memory Machines
Limited memory machines can retain some past events, allowing them to interact more deeply with the world around them compared to reactive machines.
For example, self-driving cars use a form of limited memory to make driving decisions such as turning, monitoring other vehicles, and adjusting speed. However, these machines cannot form a comprehensive understanding of the world, as their retrieval of past events is very limited and used within a narrow timeframe.
- Theory of Mind Machines
Machines that operate on the “theory of mind” represent an early form of artificial general intelligence. In addition to creating representations of the world, these machines can understand the existence of other entities within that world. However, this type of AI is still not fully realized.
- Self-Aware Machines
Self-aware machines are theoretically the most advanced type of artificial intelligence. These machines can understand the world, others, and themselves. This concept is what comes to mind when discussing the achievement of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). However, realizing this reality remains out of reach for now.
Artificial intelligence is one of the most prominent technologies shaping the future, with its ability to perform tasks that previously required human intelligence.
While the development of this technology continues at a rapid pace, achieving Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) remains out of reach; however, the possibility of attaining it opens new horizons for the future of human-machine interaction.
This progress must be accompanied by an awareness of its challenges and potential risks to ensure that this technology can enhance human life and promote balanced and sustainable technological and economic development.


















