In our connected world, cybersecurity is one of the biggest challenges organizations face nowadays, as evolving cyber threats and malicious cyberattacks put systems and data at constant risk.
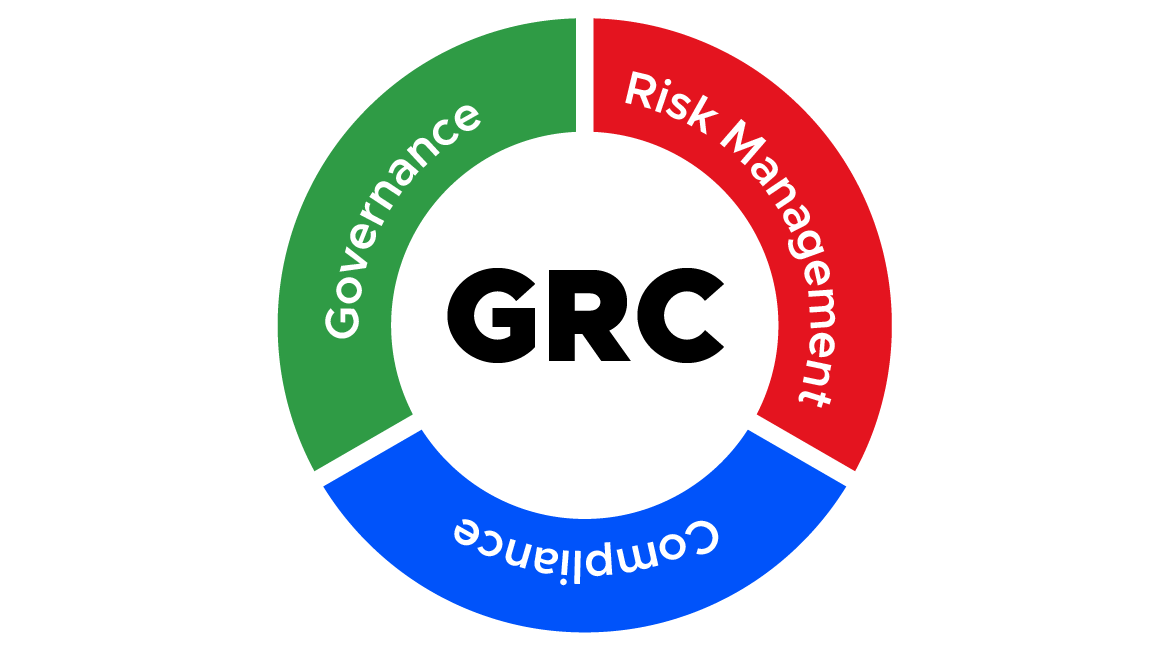
To address this challenge, cybersecurity’s Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) framework is a comprehensive solution that ensures effective protection and strong compliance for organizations.”
If you want to learn more about how to implement the GRC framework in cybersecurity and its potential benefits, don’t skimp on this article.
First thing
What is the Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) framework?
The Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) framework in cybersecurity is a comprehensive approach to managing an organization’s cybersecurity risk, encompassing a set of policies, procedures, and practices that help organizations manage risks associated with IT systems, data assets, and digital operations.
The Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) framework in cybersecurity is designed to provide a comprehensive approach to managing cybersecurity risks, including identifying and assessing risks, developing risk management strategies, monitoring compliance with regulations and standards, and responding to incidents and violations.
now
What do the terms governance,risk,” and compliance refer to?
- Governance: Governance refers to the comprehensive management of cybersecurity risks within an organization, including the development of risk management policies, procedures, and guidelines, defining cybersecurity responsibilities, and providing oversight and accountability in the area of risk management.
- Risk: Risk management involves identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks associated with an organization’s IT systems, data assets, and digital operations, and this includes developing risk mitigation strategies to reduce the likelihood and impact of cybersecurity incidents.
- Compliance: Compliance refers to the process of ensuring that an organization’s cybersecurity practices and policies comply with relevant regulations and standards, including monitoring compliance with regulatory requirements, reporting on compliance, and ensuring that an organization is prepared to respond to security audits and assessments.
Now we move on to the steps involved in developing the GRC framework.
The key steps to developing a cyber security governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) framework are:
Developing a governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) framework in cybersecurity involves a comprehensive approach consisting of multiple steps. Below are some general steps that can guide you in developing a cyber security GRC framework:
- Scope and objectives Definition: The first step is to define the scope and objectives of the GRC framework in cybersecurity. This includes identifying the business processes, information technology systems, and data assets that need protection, as well as the regulatory requirements and compliance obligations that must be met.
- Governance Structure Development: Establishing a governance structure that defines the roles and responsibilities of key stakeholders, including the board of directors, senior management, and IT personnel This involves developing policies and procedures to manage cybersecurity risks and setting metrics to measure performance.
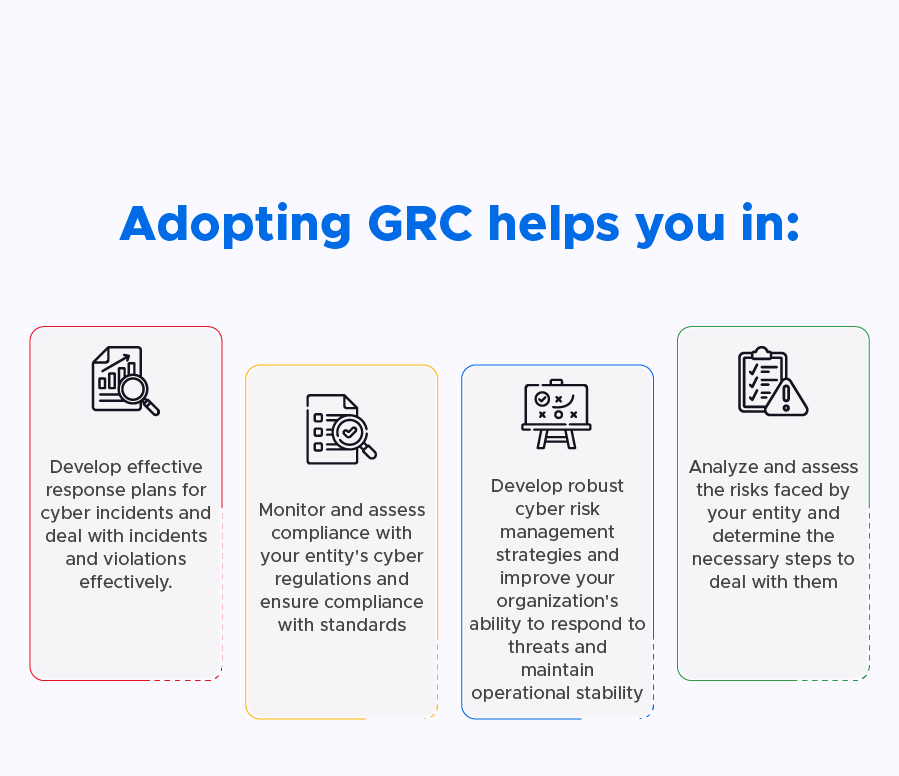
- Risk Assessment: Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify risks and potential vulnerabilities in the organization’s IT systems and data assets. This includes determining the likelihood and potential impact of various cybersecurity incidents.
- Risk Management Strategies Development: Based on the results of the risk assessment, develop risk management strategies that prioritize the identified risks and vulnerabilities. This includes implementing technical and organizational controls to mitigate the likelihood and impact of cybersecurity incidents.
- Establishing a Compliance Monitoring and Reporting System: Track the performance of the Cyber Security GRC framework in light of regulatory requirements and compliance obligations. This includes developing performance metrics and indicators to monitor and track the effectiveness of the cyber security GRC framework and reporting them to senior management and other stakeholders.
- Continuous Evaluation and Improvement: Cyber threats evolve constantly, so it is important to regularly assess and improve your framework. Conduct regular assessments to identify vulnerabilities and areas for improvement, and update your policies and procedures accordingly.
- Conduct Regular Testing and Assessment: Conduct regular testing and assessment of the Cyber Security GRC framework to ensure its effectiveness in managing specific cybersecurity risks. This includes performing penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and security audits to identify weaknesses and security gaps.
Key Features of Developing an Effective Cyber Security GRC Framework
- Comprehensive Risk Assessment: The framework should provide a comprehensive risk assessment that identifies potential risks, their likelihood, and their impact on the organization.
- Compliance Management: The framework should ensure the organization’s compliance with all relevant regulatory and legal requirements and provide mechanisms for monitoring and reporting compliance.
- Security Controls: The framework should include security controls that address identified risks and provide a framework for their implementation and management.
- Incident Management: The framework should provide a clear process for incident management, including reporting, investigation, and remediation.
- Data Protection: The framework should ensure the protection of data through measures such as encryption, backup, and appropriate recovery.
- Third-Party Risk Management: The framework should address risks associated with third-party service providers, including assessing their security posture, monitoring compliance, and defining contractual requirements.
- Employee Awareness and Training: The framework should provide regular awareness and training for employees on cybersecurity risks.
- Continuous Improvement: The framework should include regular assessments to identify vulnerabilities and areas for improvement and be updated accordingly to stay abreast of evolving cyber threats.
Conclusion:
In a world full of evolving cyber challenges and threats, information security cannot be taken lightly. This is where trusted companies like Renad Al-Majd (RMG), a leading company in Saudi Arabia, come into play by offering advanced and reliable cybersecurity services. Renad Al-Majd is the optimal choice for entities and organizations seeking to protect their data and resources from electronic threats. They provide integrated solutions in the field of cybersecurity, ranging from security assessments and vulnerability analysis to the design and implementation of customized security strategies.